Access to HTML DOM
Basic code
Consider an html file containing this code
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" > <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <title> My Webpage </title> <script src="script.js" defer></script> </head> <body> <div class="myElement"></div> </body> </html>
Check that this page leads to an empty blank webpage when viewed from the browser.
> Now create a file called script.js (in the same directory than your html file).> Add the following JavaScript code in this file script.js
"use strict;" const element = document.querySelector(".myElement"); element.textContent = "Hello World";
Reload the webpage in the browser and check that the sentence "Hello World" is now appearing.
Explanation
Let first check at the JavaScript syntax
"use strict;"
- - This is a header syntax indicating you are writing JavaScript code following the most recent version. The recent version is more strict than the outdated one, and it is a good practice to use it.
-
- In your case, you should always start your JavaScript file by this header line, even if it is not explicitely written.
const element = document.querySelector(".myElement");
- - document is a globally accessible variable that contains the DOM of the HTML webpage.
-
-
The HTML DOM (Document Object Model) can be understood as the tree of elements corresponding to the structure of the HTML webpage.
-
The HTML DOM (Document Object Model) can be understood as the tree of elements corresponding to the structure of the HTML webpage.
-
- document.querySelector("X") (doc MDN, W3School) allows to query inside the DOM an element matching the provided selector. The syntax of the selector "X" is similar to CSS.
- - const element = document.querySelector(...) defines a variable named element. element receives the value returned by "document.querySelector(...)". Also, element is declared as const which means that element cannot be re-assigned in the future to another value (note that the data inside element can still be modified).
element.textContent = "Hello World";
- - Modifies the textual content of the DOM element stored in the variable element.
Finally, in the HTML file, the line
<script src="script.js" defer></script>
enables to load the JavaScript file. The defer keyword indicates that the script should run once the HTML DOM element is loaded.
As a result, the HTML code is first parsed by the browser, and the DOM tree is built, before the script in script.js is executed.
Loop
Add the following loop in the JavaScript and check the result on the webpage.
for(let k=0; k<20; k++) { element.textContent += "Hello World "; }
Note that it is possible to use JavaScript to automatize tasks such as in using loops to fill and generate content, while this was not possible in pure HTML and CSS description.
Browser console
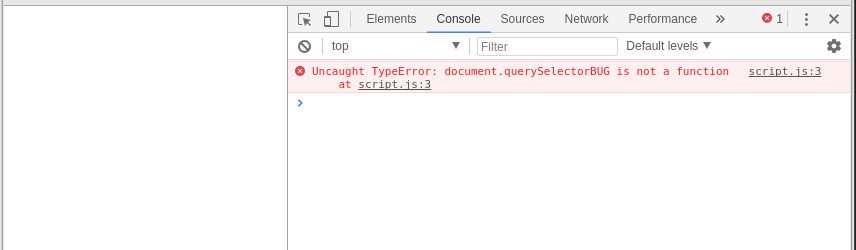
Let's consider that your JavaScript code contains a syntax error or bug. This error may result in a complete empty screen that can be hard to debug without extra information.
To help developers to debug and follow the execution of JavaScript code, modern browsers propose an embedded console where information and error can appear, similarly to standard console output in other languages.
Modify the first line of your JavaScript code into the following erroneous one
const element = document.querySelectorBUG(".myElement");
-
- Observe that the resulting webpage is now an empty one, without visible error information.
-
- Enter the developer mode of your browser, usually with the shortkey F12. And select Console.
- - Observe that the console is now indicating the source of the error, thus helping to debug.
More generally, you can use the command console.log(), which is similar to print statements of other languages.
Consider the following code
const element = document.querySelector(".myElement"); element.textContent = "Hello World"; for(var k=0; k<20; k++) { console.log("k=",k); element.textContent += "Hello World "; } // any variable can be printed in console console.log(element.textContent);
HTML template
In the future, you may start with the following valid HTML template for webpage with css and JavaScript. Adapt the title, and names of CSS and JavaScript files to your needs.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="style.css"> <script src="script.js" defer></script> <title> My Webpage </title> </head> <body> </body> </html>